COVID-19 Vaccines– There are 33 vaccine approved by at least one country. Covaxin of Bharat Biotech Approved by 13 countries) and Covishield Oxford/AstraGeneca formulation (approved in 47 countries) have been widely used in India. Sputnik V of Russia approved in 74 countries) was also used in India. All these required 2 jabs. Later Sputnik Light approved in 26 countries) was also approved. Sputnik Light is a safe and approved stand-alone one-shot vaccine against COVID-19. Both Sputnik V and Sputnik Light are created by the Gamaleya Center. Janssen covid vaccine of Johnson & Johnson has been approved in 106 countries. Spike vax of Moderna has been approved in 86 countries. Caomirnaty of Pfizer/ BioNtech is approved in 137 countries. Covilo of Sinopharm, Beijing has been approved in 8 countries. Coronavac of Sinovac is approved in 53 countries. The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (approved by 36 countries) , sold under the brand names Nuvaxovid and Covovax countries), among others, is a subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Novavax and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI).
Top 3 Covid Vaccines by approval
- Caomirnaty of Pfizer/ BioNtech is approved in 137 countries
- Highest Approval- Janssen Covid vaccine of Johnson & Johnson has been approved in 106 countries.
- Spike vax of Moderna has been approved in 86 countries
- The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) is a global partnership launched in 2017 to develop vaccines to stop future epidemics.
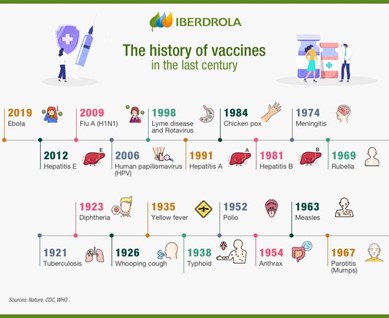
IPV or Salk vaccine – Polio is a virus that paralyzes 1 in 200 people who get infected. Among those cases, 5 to 10 per cent die when their breathing muscles are paralyzed. There is no cure for polio once the paralysis sets in – only treatment to alleviate the symptoms. Oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) or Sabin vaccine was also developed subsequently.
MMR – This is measles vaccine .Measles is a highly contagious disease with symptoms that include fever, runny nose, white spots in the back of the mouth and a rash. Serious cases can cause blindness, brain swelling and death.
MMR– This vaccine is used against Mumps which can cause headache, malaise, fever, and swollen salivary glands. Complications can include meningitis, swollen testicles and deafness.
HPV– It is used against Human papillomavirus (HPV) . HPV usually has no symptoms, but some strains can cause cervical cancer – the fourth most common cancer in women. Almost all cases of cervical cancer (99 per cent) are caused by HPV. HPV can also cause genital warts in both men and women, as well as cancer on other parts of the
BCG– It is a vaccine against tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection that most often attacks the lungs, but in infants and young children, affects other organs like the brain. A severe case could cause serious complications or death.
Hep B– Hepatitis B virus is a dangerous liver infection that, when caught as an infant, often shows no symptoms for decades. It can develop into cirrhosis and liver cancer later in life.
DTP– It is used against Diphtheria which infects the throat and tonsils, making it hard for children to breathe and swallow. Severe cases can cause heart, kidney and/or nerve damage.
DTP– It is also used against Tetanus which causes very painful muscle contractions. It can cause children’s neck and jaw muscles to lock (lockjaw), making it hard for them to open their mouth, swallow (breastfeed) or breathe. Even with treatment, tetanus is often fatal.
DTP– It is also used against Pertussis (whooping cough) which causes coughing spells that can last for weeks. In some cases, it can lead to trouble breathing, pneumonia, and death.
Hib– Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib),is a bacterium that causes pneumonia, meningitis and other severe infections almost exclusively in children under 5 years old.
Pneumococcal– Pneumococcal diseases range from serious diseases such as meningitis and pneumonia to milder but more common infections like sinusitis and ear infections.
Rotavirus– Rotaviruses cause severe diarrhoea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance and shock in young children. This can lead to death if treatment, especially fluid replacement, is not immediately started.